
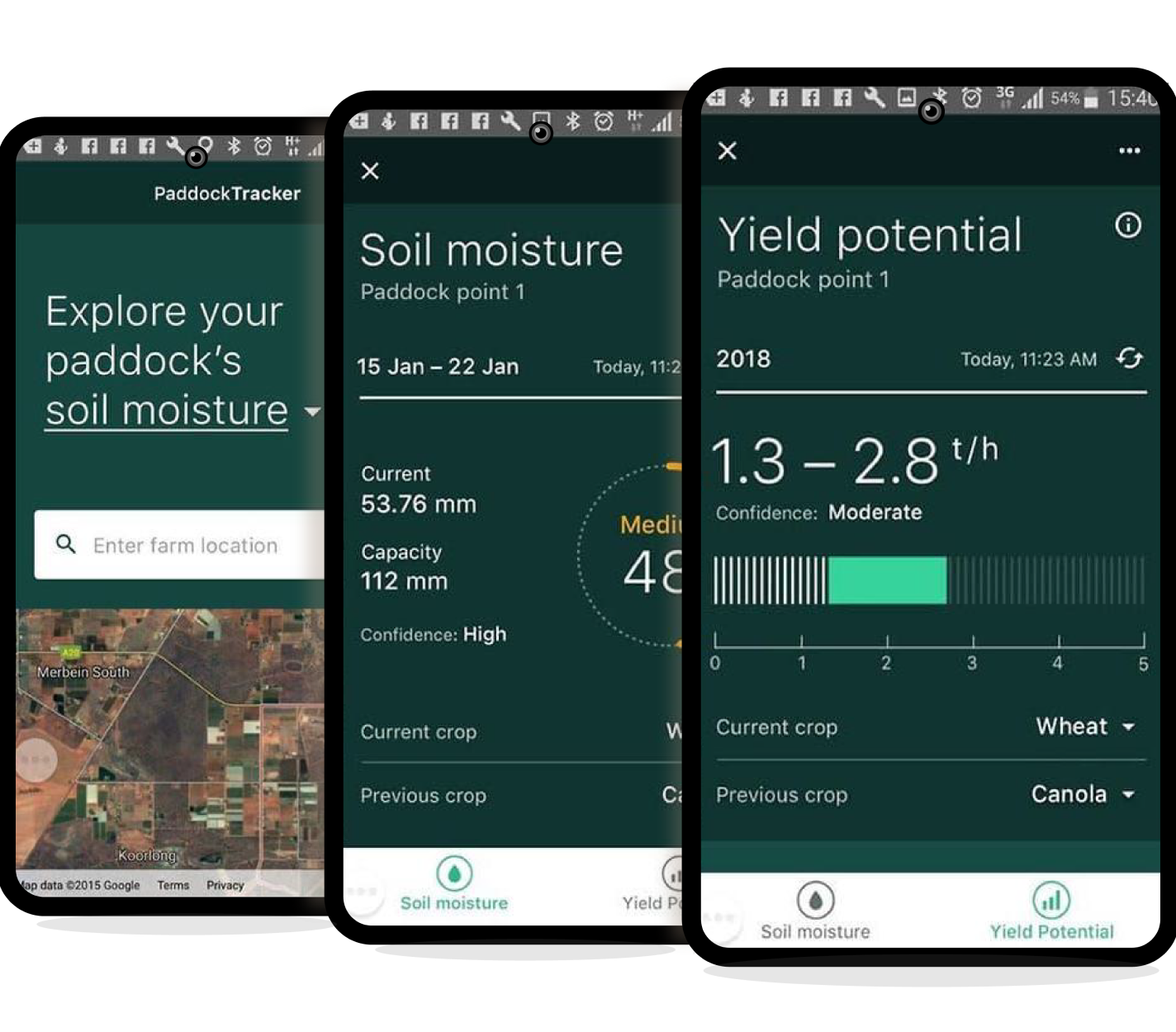
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), was facing challenges in accurately predicting the yield potential of wheat at a paddock level due to variations in soil nutrient levels, temperature changes, and weather patterns throughout the season. The organization needed a solution that could provide accurate predictions of wheat yield potential based on real-time data collection and analysis from IoT devices, while also incorporating historical data on soil nutrient levels and other parameters. The client partnered with Quantilus to develop a prototype that leveraged data collection and analysis from IoT devices to gain insights.
The client faced several problems that led to the need for a prototype that leveraged modern technology for predicting wheat yield:
Overall, the existing processes hindered the client’s ability to accurately predict wheat yield potential and optimize crop management practices.
To address the challenges faced by the client, Quantilus developed a prototype that leveraged data collection and analysis from IoT devices to gain insight into soil nutrient levels, temperature changes, and other environmental factors that impact wheat yield potential. The prototype used Machine Learning algorithms such as Linear Regression and Decision Trees to forecast yield potential based on historical data about soil nutrient levels and other parameters.
The features of the prototype included:
The IoT devices used in the prototype for paddock-level wheat yield potential had the capability to gather and transmit real-time data on various environmental factors that affect the growth and yield of wheat crops. These devices were placed in strategic locations in the field to capture data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, light intensity, and other parameters. Some of the key features of these devices included:
Overall, the IoT devices played a critical role in the prototype by providing real-time data on various environmental factors that affect the growth and yield of wheat crops. This data was then used in conjunction with Machine Learning algorithms to generate accurate forecasts and recommendations for farmers.
The client reaped multi-fold benefits from the prototype, including:
WEBINAR